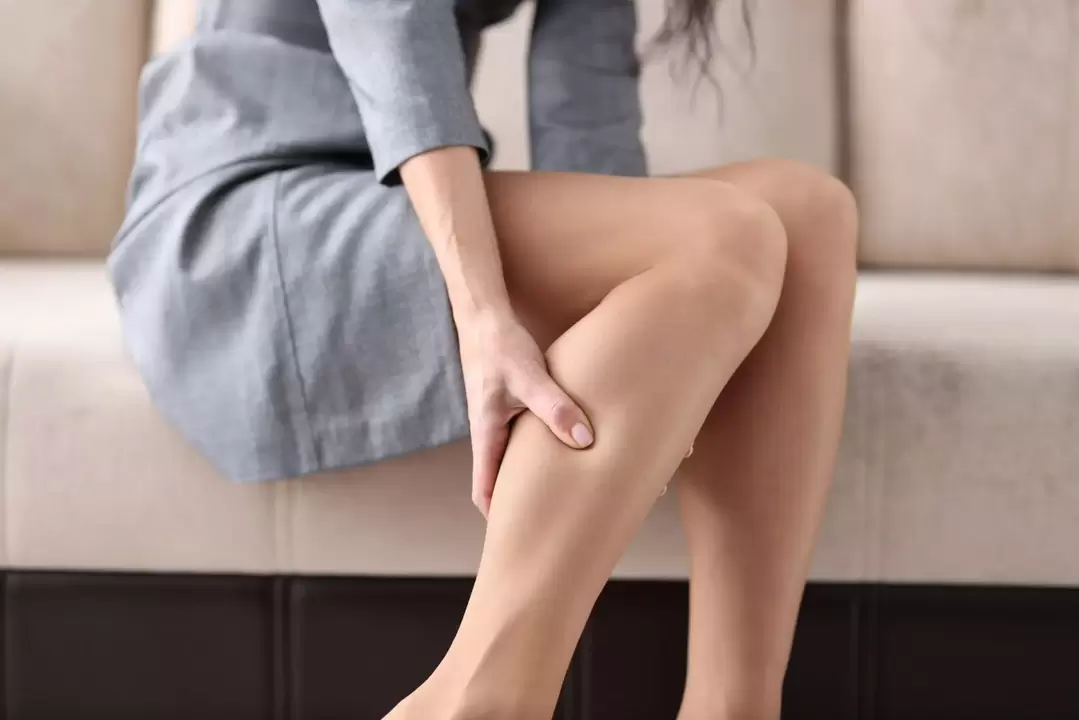
Varicose veins are a disease of the subcutaneous veins, manifested by excessive dilation and stretching, the veins lose their elasticity and blood circulation processes are disturbed. Swollen varicose veins usually appear on the legs.
Varicose veins are considered a cosmetic problem, but they can lead to complications if left untreated. The main ones are nutritional ulcers and thrombophlebitis, which occur in 70% of patients with varicose veins.
Symptoms of varicose veins
Signs that you are already in the initial stages:
- legs get tired quickly;
- burning and heaviness in the legs;
- A small swelling occurs;
- pain in the veins;
- Calf cramps.
Another characteristic of varicose veins is local pain in the calf, which appears at night and disappears in the morning. The pain is not severe, it feels moderate, pulling.
In the first stage, dilated veins are not visible, but varicose veins have formed. Sometimes it takes decades. Gradually, symptoms become more disturbing, with signs of venous insufficiency:
- Leg swelling - In patients (most commonly women with varicose veins), chronic venous disease is often accompanied by increased calf volume. At the same time, edema and pain and heaviness appear in the afternoon and subside after sleep. Foot edema is not a typical manifestation of the above-mentioned pathology, it is a symptom of lymphedema;
- itchy skin;
- knots, twists and turns, visible to the naked eye;
- The skin darkens, thickens, and develops a bluish tinge.
Symptoms worsen as venous disease progresses. The skin on the legs deteriorated with eczema and trophic ulcers.

Causes of varicose veins
The cause of varicose veins is the incompetence of the valves in the veins of the legs, so the outflow of blood deteriorates. The venous network of the legs consists of superficial and deep veins connected by blood vessels. Superficial veins carry blood away from the skin and subcutaneous structures, while deep veins carry blood away from internal organs. The veins connecting them act as compensators, equalizing the pressure in the superficial and deep blood vessels.
Proper blood flow flows from superficial to deep veins. This orientation can be provided by the movement of the surrounding muscles and the work of the vasomotor centers, as the movement from the bottom to the top contradicts the attraction.
If for some reason the outflow becomes difficult, the vessel walls become inflamed, thin, dilated veins and cyanotic nodules appear characteristic of varicose veins.
The disease develops in response to a series of adverse conditions:
- Heredity - Weakness in vessel walls can be passed down from generation to generation, resulting in loss of vascular tone;
- Exhausting work, standing – groups at risk include those who, by the nature of their activities, must sit or stand for long periods of time;
- Frequent pregnancies and deliveries - during this period, blood volume and vein compression increase, which can cause varicose veins;
- Obesity - increased venous pressure in overweight people increases the chance of varicose veins;
- Hormonal system failure - Self-administration of birth control pills and other hormone-based medications can cause changes in the walls of veins. In women, this reaction can be observed during pregnancy;
- Nutrition - Lack of fresh fruits and vegetables in the menu leads to lack of fiber and as a result - weakening of vein walls.
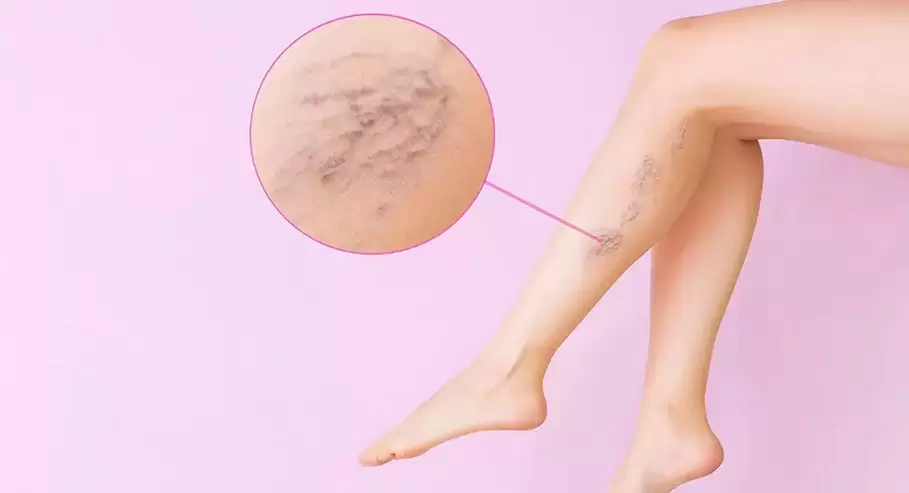
What do varicose veins look like?
Since varicose veins are deformations of veins, the disease is also known as a cosmetic problem:
- First, the patient will notice webs and veins on the legs;
- Later the veins become tortuous and lift the skin;
- In the most advanced stages, varicose nodules are clearly visible, representing dilated and entangled blood vessels.
what is the danger of this disease
What happens if the disease is left untreated? This will inevitably lead to complications. The most dangerous are thrombophlebitis and "separation" of blood clots. Similar complications occur in 5% of patients. With age, trophic ulcers often form and are difficult to treat. The risk of complications from varicose veins increases over time.
- ThrombophlebitisWith it, blood clots can form in the veins of the legs, which can rupture and block arteries, causing a heart attack.
- Venous thrombosis.A blood clot blocks a blood vessel. It manifests as pain in the legs that is exacerbated by physical exertion.
- pulmonary embolism. Detached thrombus obstructing the lumen. Death can happen within the first half hour. If the clot is small, a pulmonary infarction may occur.
- Nutritional ulcer.As the ulcer progresses, the skin darkens and thins. Occurs due to tissue malnutrition. Poor response to treatment.
risk factors
- heredity. If both parents have varicose veins, then the probability of the child getting this disease is 90%, if one has 60%.
- Pregnant.During this time, venous disease is caused by 3 factors:
- Hormonal changes - the production of high levels of progesterone relaxes muscles and makes veins more fragile;
- Increased pressure on the uterus - in connection with this, worsening of blood outflow from the legs;
- 20-30% increase in blood volume - the valves in the veins of the legs cannot bear the load, especially when they are initially weak;
- wrong nutrition.Uncontrolled consumption of processed foods, sugar and salt, fast food, fried and fatty foods, trans fats, preservatives and artificial additives in industrial products can also leave traces.
- Hormonal background.The activity of the hormone weakens the veins, causing them to dilate and preventing the valves from closing properly.
- tight clothes. Tight belts, tight jeans, and underwear interfere with the harmonious flow of blood and impede circulation.
- High heel. When walking, the veins work to the limit. This is because the load is not evenly distributed - the main share falls on the forefoot. Painful, swollen legs are the first signs of early varicose veins.
Diagnosis of varicose veins
In the early diagnosis of varicose veins, ultrasound techniques are used - vessel scans and Doppler angiography.
Ultrasound Angiography Scan (USAS) is an informative non-invasive examination of peripheral blood vessels. It makes it possible to obtain two-dimensional images of arteries, visualize intravascular structures, and assess the direction and nature of fluid flow.
In severe cases, computed tomography (CT) is used when a response cannot be obtained using USAS.
Doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound) is the easiest way to evaluate the peripheral blood vessels. He assessed arterial status by indirect indicators: blood flow response to functional tests, etc.
X-ray contrast venography is used to diagnose arteriovenous dysplasia, acute thrombosis and its consequences, and small pelvic varices.
Varicose Veins Treatment
surgical technique
Complete healing of varicose veins is possible only after surgical treatment. It is done in three ways:
- Phlebectomy - removal of enlarged varicose veins;
- Sclerosis is the introduction of a special substance into the varicose veins that "glues together" the vessel walls and normalizes blood flow. Vein swelling disappears and even cosmetic imperfections disappear;
- Laser photocoagulation - the wall of the vein is heated so that the lumen of the vein is "closed". Operate only if the vein is not dilated by more than 10mm.
Drug treatment of varicose veins
Intravenous preparations in tablet form play a leading role in treatment. They improve blood circulation processes, heal arteries.
Intravenous medications are also prescribed - phlebotonics. They cause thinning, increased permeability, decreased elasticity, and fluid stagnation in blood vessel walls. Preparations strengthen the vein wall, increase its elasticity, reduce swelling and other negative signs. Another quality of phlebotonics is the establishment of microcirculation in the affected area.
Antiplatelet drugs are used to thin the blood in the veins. Medicines needed when you need to reduce blood clots. Suitable for patients with increased blood viscosity. You should only take antiplatelet drugs if you do not have a tendency to bleed.
Anticoagulants are sometimes used to stop an individual from developing blood clots. They eliminate blood clots and reduce viscosity. But the decision is made by the attending physician after evaluating the potential health benefits and potential of rice.
compression therapy
A reliable assistant in the treatment of varicose veins is a compression garment. The working principle of the product is as follows:
- Increased pressure in superficial and deep veins when wearing compression stockings;
- The pressure at the bottom is the highest, the blood vessels are narrowed, and the blood flows out the fastest;
- Improved operation of the valve due to narrowing of the vein;
- Leg pain, swelling, fatigue disappeared.
complex method
There are many treatment options, but the most correct ones emphasize the overall improvement of the entire organism. Varicose veins in the broadest sense are not just a problem with the veins, but a symptom of something malfunctioning in the body. Therefore, we recommend that you heal your body and do it consistently and wisely.
- drink plenty of water - dehydration is one of the causes of blood clotting, especially during hot periods;
- Helps detoxify the liver - include in the diet artichokes, flax, grapefruit, oranges, apples, cruciferous vegetables, rosemary, dandelions, olives (ensure that there are no allergic reactions and individual intolerances to the product);
- Eliminate from your diet all pro-inflammatory foods that thicken the blood and adversely affect the walls of blood vessels (alcohol, coffee, sugar, pastries, dairy products, smoked foods, canned foods, fast foods, refined foods);
- Eliminates constipation - they squeeze the venous blood flow in the pelvis. Start drinking commensals or microbes. The bacteria in its composition create the balance of the microflora, which normalizes the stool. They improve the condition of the small and large intestines and the gastric mucosa;
- Analyze for homocysteine - it should not exceed 10. If it's higher, you'll need to make sure you're not deficient in vitamin B12, folic acid, and iron. At the same time, restore the microflora, otherwise their uptake could be impaired;
- Restore protein levels. For verification, a biochemical blood test is given: the optimal protein concentration for adults should be 72-86 g / l, for children - 45 to 80 g / l.
- Works with insulin resistance - This problem is often closely associated with this disease. You can recognize it by symptoms: persistent hunger and frequent urges to eat, multiple papillomas, red spots that look like moles, swelling, thirst, and high blood pressure;
- Introductory exercises - Pilates, yoga, light cardio;
- To improve lymphatic outflow - drink water with herbs, cranberries, spices, lemon, ginger;
- Take a contrast shower - under the influence of cold, small blood vessels begin to narrow, while under the influence of heat, on the contrary, they dilate. This leads to a strengthening of the walls of blood vessels and an increase in their tone.
- Restoring hormonal levels - Hormonal overactivity dilates blood vessels and prevents valves from closing properly. To support the process of restoring hormonal balance, broccoli symbiosis is suitable. The active substance it contains -- sulforaphane -- works to rid the body of excess estrogen. This is because broccoli contains anti-cancer substances such as potassium, zinc, selenium, beta-carotene, amino acids, vitamins A, C and E.